What is Liver Cancer?
Cancer affects 1 in 3 people in the United States. Chances are that you or someone you know has been affected by cancer.
Your body is made up of trillions of cells that over your lifetime normally grow and divide as needed. When cells are abnormal or get old, they usually die. However, cancer starts when something goes wrong in this process and your cells keep making new cells and the old or abnormal ones don’t die when they should. As the cancer cells grow out of control, they can crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for your body to work the way it should.
When cancer starts in the liver, it is called liver cancer. Each year in the United States, about 25,000 men and 11,000 women get liver cancer, and about 19,000 men and 9,000 women die from the disease. The percentage of Americans who get liver cancer rose for several decades but is now declining. Liver cancer is more common in other parts of the world than in the United States.
Several types of cancer can form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.
Liver Cancer Q & A
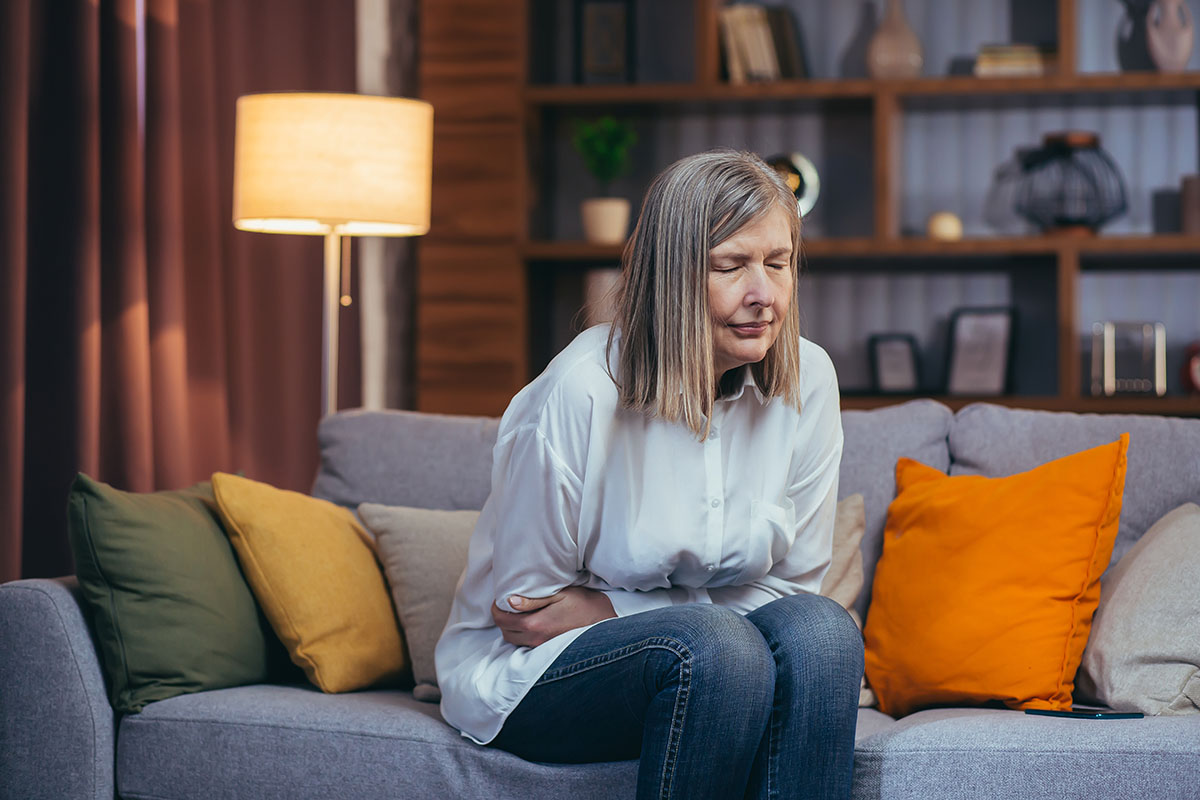
Signs and symptoms of liver cancer may include upper abdominal pain, abdominal swelling, nausea and vomiting and a hard lump on the right side just below the rib cage.
Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
- Chronic infection with HBV or HCV. Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) increases your risk of liver cancer.
- Cirrhosis. This progressive and irreversible condition causes scar tissue to form in your liver and increases your chances of developing liver cancer.
- Certain inherited liver diseases. Liver diseases that can increase the risk of liver cancer include hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease.
- Diabetes. People with this blood sugar disorder have a greater risk of liver cancer than those who don’t have diabetes.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. An accumulation of fat in the liver increases the risk of liver cancer.
- Exposure to aflatoxins. Aflatoxins are poisons produced by molds that grow on crops that are stored poorly. Crops, such as grains and nuts, can become contaminated with aflatoxins, which can end up in foods made of these products.
- Excessive alcohol consumption. Consuming more than a moderate amount of alcohol daily over many years can lead to irreversible liver damage and increase your risk of liver cancer.
- Obesity or being overweight
- Smoking
Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cancer
- Losing weight without trying
- Loss of appetite
- Upper abdominal pain
- Hard lump on the right side just below the rib cage
- Nausea and vomiting
- General weakness and fatigue
- Abdominal swelling
- Yellow discoloration of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice)
- White, chalky stools
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Intentional Oncology Treatment Options for Liver Cancer
There are several specialties that treat liver cancer and offer a variety of treatment options including open surgery. Dr. Navid Eghbalieh specializes in interventional oncology and the following minimally invasive treatments for liver cancer:
- Liver Cancer Chemoembolization (TACE)
- Y90 Radioembolization
- Ablation
- Cryotherapy
If you or a loved one have been diagnosed with liver cancer, call our office to schedule an appointment and let our team help you decide which option would be best for you.