Ultrasound
The Essential Guide to Ultrasounds at SCMSC
Ultrasounds are a pivotal tool in modern healthcare, offering a non-invasive peek into the human body’s inner workings. Utilized across many medical specialties, ultrasounds help diagnose, monitor, and sometimes treat various conditions. But what exactly are ultrasounds, and why are they so important in medicine today? Let’s dive in to uncover the versatile world of ultrasounds, exploring their types, uses, and the crucial role they play in patient care.
What are ultrasounds?
Ultrasounds, in the context of medical imaging, employ sound waves with frequencies much higher than what the human ear can hear — typically above 20,000 hertz. Unlike X-rays, which use ionizing radiation, ultrasounds make use of sound waves to create images, making them a safer alternative for a broad spectrum of patients including expectant mothers and young children.
The principle behind ultrasounds is simple yet profound. An ultrasound machine emits high-frequency sound waves into the body through a device known as a transducer. These sound waves travel until they encounter tissues, organs, or fluids, at which point they bounce back to the transducer. The machine then interprets these echo patterns and translates them into visual images, known as sonograms.
This sophisticated interplay of sound waves and echoes allows healthcare providers to see inside the human body in real-time. The images generated can reveal valuable information about the structure and function of organs and tissues. It can also show movement, such as the pumping action of the heart or the progress of a fetus in the womb, offering a dynamic insight into the body’s internal operations.
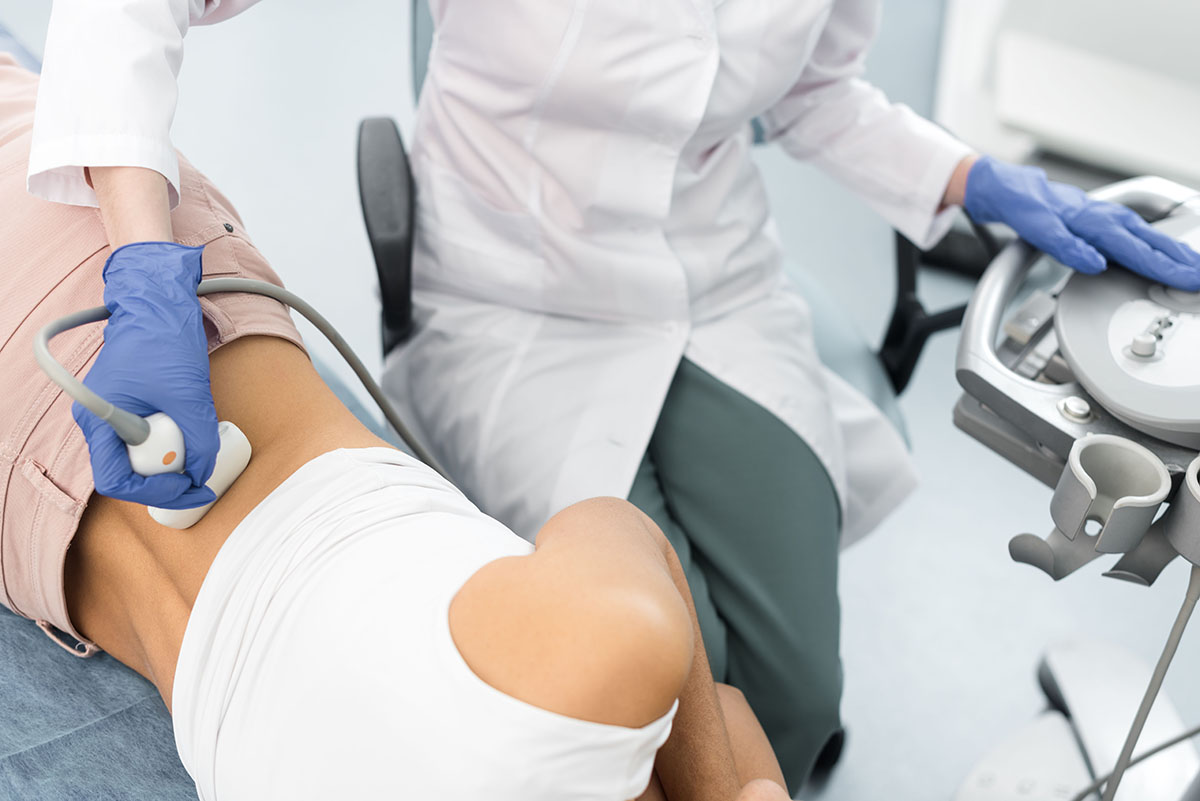
Ultrasounds may be used to provide a non-invasive examination of many inner workings of the body, including the thyroid.
Key Components of Ultrasound Technology
- Transducer Probe: This is the handheld device that sends and receives sound waves. Depending on the area of the body being examined, different types of transducers with varying shapes and sizes are used.
- Gel: A special gel is applied to the skin where the ultrasound is being performed. This helps eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin, ensuring the sound waves travel more efficiently into the body.
- Control Panel: Ultrasound machines feature a console containing a keyboard and screen, allowing the operator to adjust settings and capture specific images for evaluation.
- Display: The real-time images produced by the ultrasound are displayed on a monitor, providing a window into the body’s interior landscape.
Each component plays a crucial role in ultrasound technology, coming together to form a system that is invaluable in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions. From monitoring fetal development to evaluating heart conditions and guiding minimally invasive procedures, ultrasounds offer a versatile and safe diagnostic tool. As advancements in technology continue to evolve, the capabilities and applications of ultrasounds will expand, further solidifying their importance in medical imaging.
Why ultrasounds matter
Ultrasounds stand out for their safety and versatility. They are radiation-free, making them an ideal choice for a wide range of patients, including pregnant women.
Ultrasounds aid in:
- Monitoring fetal development and health
- Diagnosing conditions in organs like the heart, liver, kidneys, and more
- Guiding procedures such as needle biopsies
- Evaluating blood flow and detecting blockages
- Helping in the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal injuries
This technology’s non-invasive nature, coupled with its diagnostic capabilities, makes ultrasounds indispensable in contemporary medicine.
Types of ultrasounds
Ultrasounds are not one-size-fits-all; they come in various forms to suit different diagnostic needs:
- Standard Ultrasound: Produces two-dimensional images ideal for evaluating fetal development and examining abdominal organs.
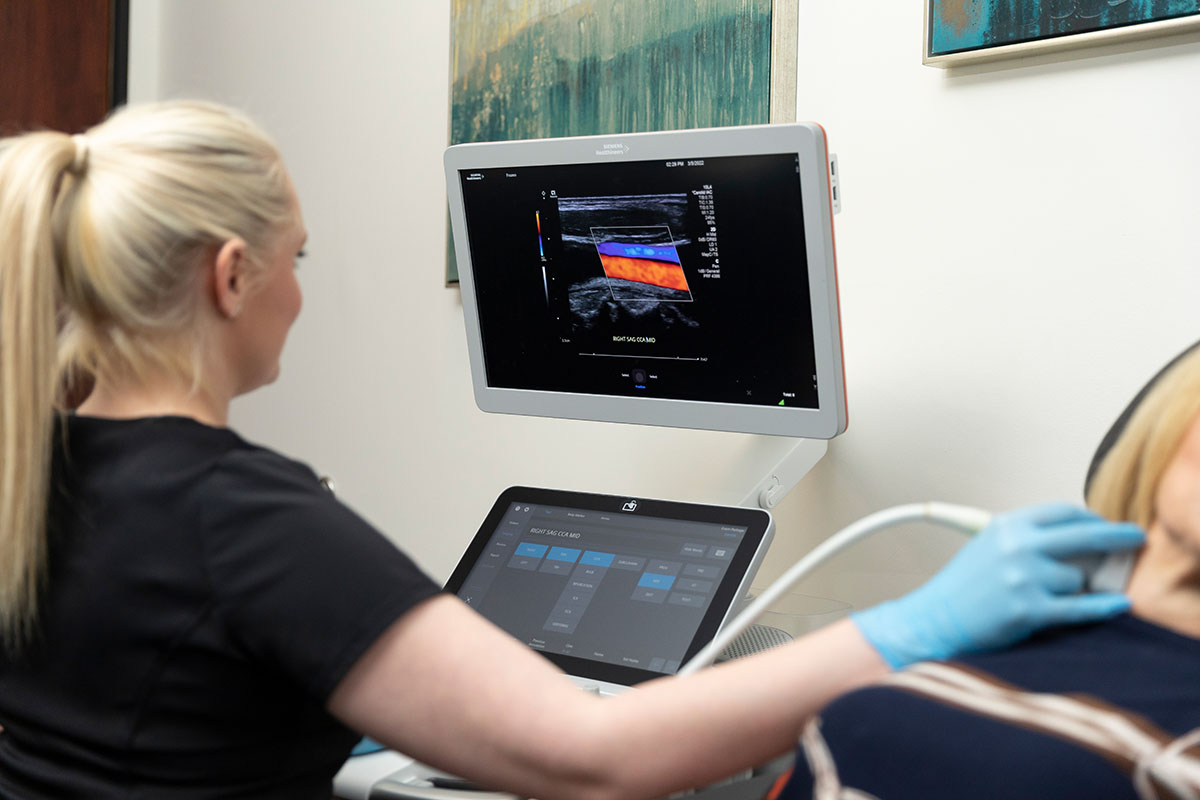
- Doppler Ultrasound: Measures blood flow in arteries and veins, crucial for detecting blockages or narrowing of vessels.
- 3D and 4D Ultrasounds: Offers a more detailed and dynamic view of the fetus, often used in specialized prenatal care.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Provides a clearer view of female reproductive organs.
- Echocardiograms: Specifically tailored for the heart, giving detailed images of heart structure and function.
Ultrasound technology advancements
Make an appointment at SCMSC
We look forward to welcoming you
Schedule an evaluation with the doctors at Southern California Multi-Specialty Center.