Pulmonary Embolism Surgeon Los Angeles
“Sudden death is the first symptom in about one quarter (25%) of people who have a PE.”
– Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
An embolus is a blood clot that breaks off and moves to another part of the body. If that clot or embolus ends up traveling to the lungs, it is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). The clot can restrict blood flow to the lungs. This event can be life threatening if not treated immediately. Since PE is generally linked to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) the combined condition is called venous thromboembolism (VTE).
Pulmonary Embolism Q & A
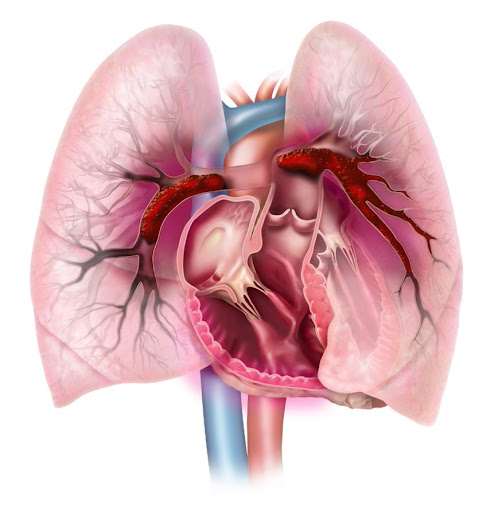
Image of large clots sitting in both lungs restricting blood flow. Image provided courtesy of Boston Scientific. ©2022 Boston Scientific Corporation or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
An embolus is a blood clot that breaks off and moves to another part of the body. If that clot or embolus ends up traveling to the lungs, it is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). The clot can restrict blood flow to the lungs. This event can be life threatening if not treated immediately. Since PE is generally linked to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) the combined condition is called venous thromboembolism (VTE).
Risk Factors for Pulmonary Embolism
- Smoker
- Pregnant or postpartum up to 6 weeks
- History of heart failure or stroke
- History of deep vein thrombosis
- Varicose veins
- Birth control or hormone therapy
- Obese
- Sitting or inactive for a long period of time
- History of clots
- Cancer or chemotherapy
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
- Sudden shortness of breath that gets worse with exertion
- Coughing up blood
- Fever
- Fainting
- Lightheaded/ dizzy
- Chest pain that gets worse with coughing or deep breath
- Irregular or fast heartbeat
Treatment Options for Pulmonary Embolism
Depending on the severity of your case, your physician may be able to treat your PE with blood thinners or IV clot-busting medications. However, in more severe cases, you may require surgical treatment.
The surgery options for a pulmonary embolism include:
- Pulmonary embolectomy
Surgical removal of the pulmonary embolisms. - Percutaneous thrombectomy (EKOS, Penumbra, Inari)
The use of a catheter to the site of the embolism by using X-ray guidance. The catheter is a long, thin, hollow tube.
To schedule an evaluation at Southern California Multi-Specialty Center, call 818-900-6480.
Our Vascular & Endovascular Surgeons
It's important to remember not all physicians are trained in advanced vascular and endovascular surgery. It’s a good practice to get multiple opinions and do research on the surgery and the physician.
Make an appointment at SCMSC
We look forward to welcoming you
Schedule an evaluation with Dr. Eghbalieh or Dr. Abi-Chaker at Southern California Multi-Specialty Center.